INSTANT ON NOW AVAILABLE - Experience Time to first frame as quick as 2 SECONDS
4 Ways Game Engines Accelerate the Creation of 3D Training Simulations
Employee training has evolved from one-on-one training on the factory floor to classroom training sessions to simulators. Today, a new evolution - or more accurately, a revolution - is taking place in the employee training world.
With an increasingly global workforce connecting through remote collaboration tools, employers are turning to virtual reality, augmented reality, and interactive 3D streaming to provide their workforce with the skills training they need.
For professionals with highly technical, hands-on roles, accurate, photorealistic content is essential. But creating this content is easier said than done. This is where game engines like Unity and Unreal have stepped up to simplify the process.
1. Game engines are the bridge between hardware and content
Game engines have become the bridge between hardware and content. Game engines are to 3D content creation what word processors are to document creation. This is exciting news for game designers and instructional content developers alike. High quality 3D content can be designed once and used across multiple platforms.
Related Read: Top online resources for creating real-time 3D with Unity or Unreal
Rather than reinventing the wheel, instructional design creative agencies can access commonly used tools across all industries for their projects. Standard tools for shading, collision detection, acoustics, path planning, and more can be incorporated using one main suite of tools. Game engines give interactive 3D content designers a graphics engine, physics engine, audio engine, AI engine and more all in one platform
2. Game engines eliminate the need for a massive budget & large programming team
When the U.S. military decided to create visual, interactive content to train its people through storytelling, it gave the University of Southern California $45 million to create a research center for advanced military simulations, called the Institute for Creative Technologies. In other words, the talent needed to create such content was so niche, the government had to fund a defence project over 2000 miles away from the Pentagon.
This isn’t necessary today. Game engines have democratized the ability to create immersive 3D scenes and objects. Rather than compiling a team of programmers and 3D artists, creative agencies can hire individuals specifically training to use game engines that provide all the assets and tools required to bring pre-construction property projects to life.
3. Companies can create enough content to make the most of their VR investment
VR headsets are not cheap. They can cost upwards of $300 each. This means that they need to be well-utilized for training purposes in order to recoup the initial investment. In the past, creating interactive 3D content was both time- and data-intensive, limiting the amount of content available for VR headsets.
On the other hand, game engines have accelerated standard workflows, allowing companies to commission a greater number of interactive 3D training scenarios for their teams.
With faster 3D content creation, a retailer like Wal-Mart, which recently announced its intended purchase of VR headsets for over 4,600 stores, can create a wider variety of training scenarios. This includes scenarios like how to handle belligerent customers, how to cordon off and clean up a spill, how to respond during an emergency or environmental disaster, and more.
4. Game engines provide interactive 3D content for alternatives to VR headsets
While VR headsets are engaging, they also have some drawbacks. For one thing, they’re expensive. Depending on the complexity of your industry, developing high-tech VR training simulators can cost tens of thousands of dollars.
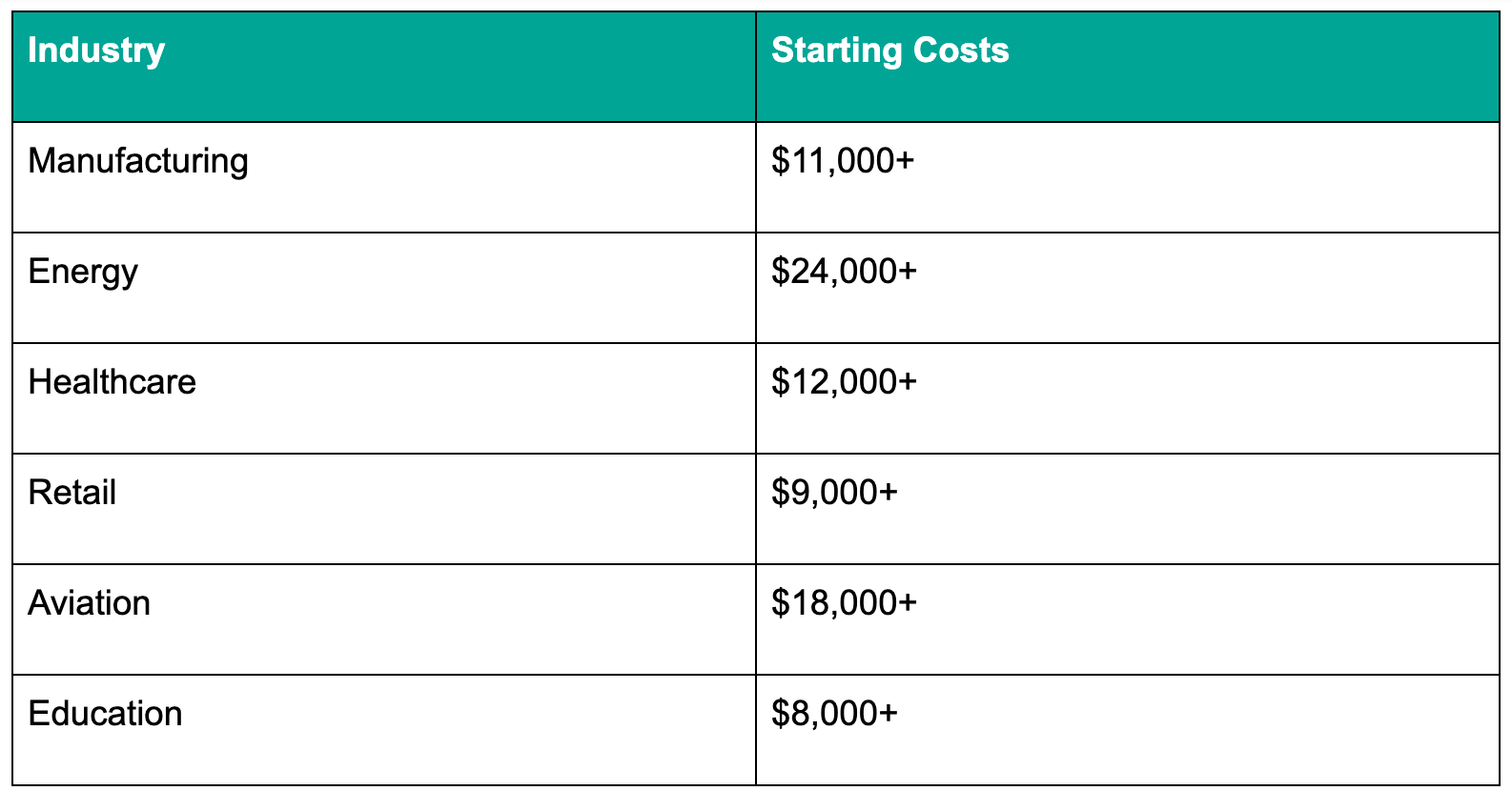
Table: Starting costs of creating a VR training simulator across industries. (Source)
In addition, they don’t necessarily eliminate travel costs, which are a huge training-related cost center. In 2018, U.S. companies spent $29.6 billion on travel, facilities, and equipment for training purposes. VR equipment is often securely stored in specific locations, so employees still need to travel to VR training sites.
Read Next: Does photo-real 3D for business need VR or real-time mobile access
Finally, VR training is only as valuable as the number of employees who use it. For VR, one malady in particular presents a roadblock for even the most motivated worker: virtual reality sickness. Currently, 40 to 70 percent of VR users experience motion sickness. With some VR applications, this number shoots up to 100 percent.
The good news is that game engines are not a VR-specific 3D content creator. On the contrary, game engines allow creative agencies to create 3D scenes for a variety of mediums including interactive 3D streaming and augmented reality. Your 3D training modules can be shared via a laptop, tablet, or mobile device with a simple link instead of a VR headset.
Game engines offer both accessibility and flexibility
Whether you’re working with a handful of 3D content creators or a large, dedicated enterprise team, game engines provide both accessibility and flexibility.
On the one hand, game engines like Unity and Unreal provide a number of out-of-the-box tools for creative agencies to jump right in and start creating. On the other hand, experienced content creators have the freedom to do more since both game engines provide access to the source code. Unreal makes their source code available to all users while Unity only makes it available for users with Pro or Enterprise Plans.
Interested in learning more about the role of game engines in interactive training content? Download our latest white paper "Cloud streaming 3D training simulators for a mobile workforce."


